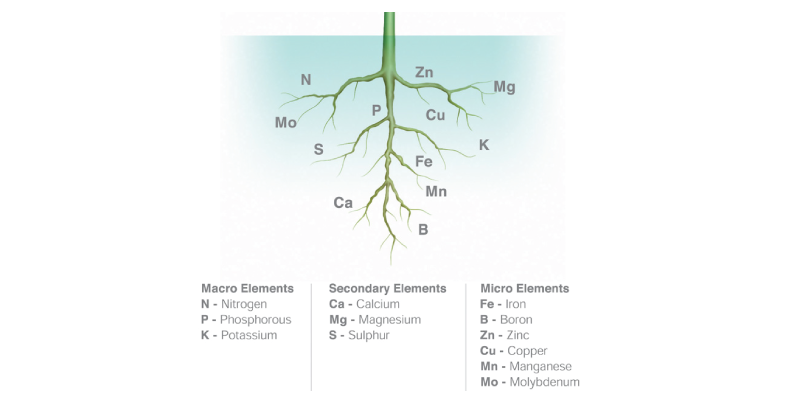
Nutrients Found in Hydroponics
Plants in hydroponics, do not live in soil. Therefore, they must gain their nutrients through water, fertilizers, and the medium the plants are submerged in. The most common nutrients such as hydrogen, oxygen and carbon are absorbed from air and water. Mineral nutrients are dissolvable in the water solution. Below is a list and description of nutrients found in hydroponics, and the growing of them.
Boron
Allows cells to divide
Permits protein formation
Active role in pollination
Creates seed production
Calcium
Fundamental to cell manufacturing and cell growth
Too much calcium will stunt growth
Moves slowly in plant
Deficient signs: will turn brown and die
Concentrated in roots and older growth
Copper
Catalyst (increases rate of reaction) for enzymes
Excess signs: will cause death
Shortage will make new growth will, and cause irregular growth
Is a fungicide
Wards off insects and diseases
Iron
Catalyst for chlorophyll production
Lack of iron turns leaves yellow/white
Reactions are used in photosynthesis
Difficult for plants to absorb
Magnesium
Central atom in chlorophyll molecules
Utilization of nutrients,
Nurtirlizes acids and toxin compounds
Deficit signs: older leaves yellow from center outward
Essential to absorption of light energy
Leaf tips will curl and discolor
Growing tips turn lime green
Manganese
Reduces nitrates before producing proteins
Deficient signs: turns young leaves molted and brown
Molybdenum
Helps form proteins and aids plants ability to pull nitrogen from air
Deficit signs: leaves turn pale and fringed appear scorched and irregular leaf growth
Nitrogen
Primary to plant growth
Convert element into proteins for cell growth
Responsible for leaf and stem growth, size and vigor
Deficient signs: new growth becomes weak ad spindly Older leaves turn yellow and die
Excess: soft, weak growth and delay flower and fruit production
Phosphorus
Necessary for photosynthesis
Highest levels during germination, seedling growth, flowering
Works as a catalyst for energy transfer
Helps build strong roots
Deficiency signs: leaves turn deep green on stunted plants, leaves show brown or purple spots
Vital for flower and seed production
Potassium
Manufacture and movement of sugars and starches
Regulates stomata openings
Growth by cell division Increases chlorophyll in foliage
Necessary during all growth stages
Encourages strong root growth, water uptake, and triggers enzymes that fight disease
Sulphur
Component of plant protein and root growth
Adds flavor and odor to plants
 Packaged Chillers Non-expandable (integrated pump tank) 1.5Ton – 20Ton Single / Dual Circuits Single / Dual Pumps |
 SAE Series Modular Chillers Expandable (pump & tank on separate skid) 1.5Ton – 200Ton Single / Dual Circuits |
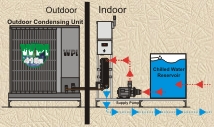 SAR Series Split Chillers Expandable (Outdoor Condensing Unit) (pump, tank, evaporator on indoor skid) 1.5Ton – 200Ton Single / Dual Circuits |